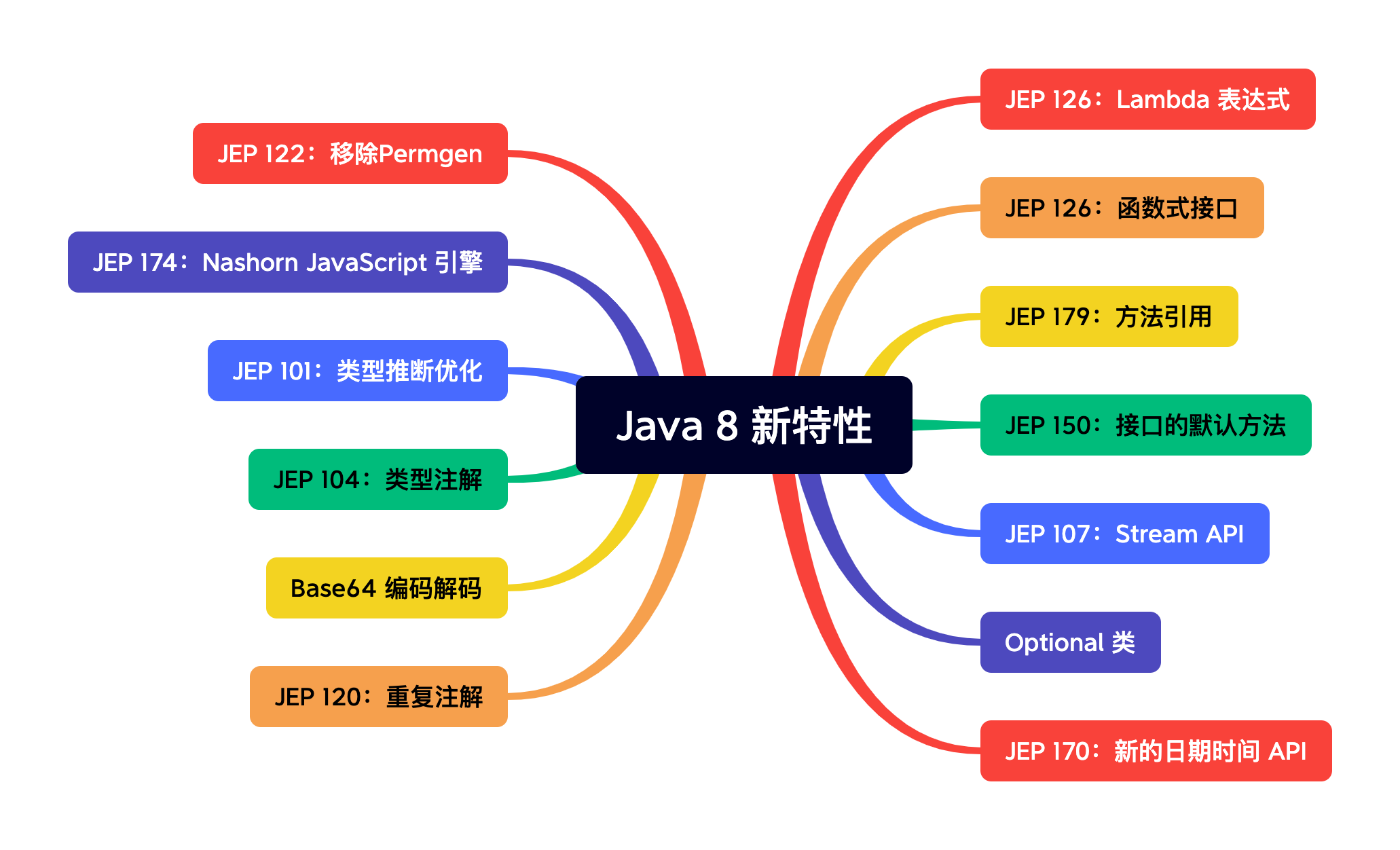
函数式接口其实本质上还是一个接口,但是它是一种特殊的接口:SAM类型的接口(Single Abstract Method),在这个接口里面只能有一个抽象方法。
当开发者在编写Lambda表达式时,也会随之被编译成一个函数式接口。Lambda表达式只是语法糖,我们只要理解函数式接口,才能读懂和用好Lambda表达式。
定义
- 有且只有一个抽象方法的接口。但它可以包含多个默认方法和静态方法。通常情况下,使用 @FunctionalInterface 注解来标识一个接口为函数式接口,这样做的目的是在编译时强制规范定义
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyFunctionalInterface {
void singleAbstractMethod();
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a default method");
}
static void staticMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a static method");
}
void doSomething();
}
|
常用的函数式接口
使用Lambda表达式,一定有函数式接口的支持;但是如果我们每一个Lambda表达式都要自己创建一个接口,这样很造成很大的不便。为了避免重复造轮子,java8常用的函数式接口都帮我们定义好,拿来直接使用即可。如果这些常用的接口不能满足需求时,这时才需要 自定义函数式接口。
Function<T, R> 函数型接口
表示接收一个参数并返回结果的函数。该函数式接口方法为R apply(T t):
示例1:函数式接口可以被new出一个实例来,必须实现其抽象接口
static void functionDemo1() {
Function<Integer, String> function = new Function<Integer, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Integer integer) {
return integer.toString() + "程序员节";
}
};
System.out.println("functionDemo1 --> " + function.apply(1024));
}
示例2:可以使用Lambada表达式简化函数式接口
static void functionDemo2() {
Function<Integer, String> function = (integer) -> {
return integer.toString() + "程序员节";
};
System.out.println("functionDemo2 --> " + function.apply(1024));
}
示例3:Lambada表达式入参只有一个时,可以不加小括号;方法体内只有一行代码时可以不加大括号和 return 关键字,直接编写返回结果即可
static void functionDemo3() {
Function<Integer, String> function = integer -> integer.toString() + "程序员节";
System.out.println("functionDemo2 --> " + function.apply(1024));
}
示例4:函数式接口做为方法的入参
static void functionDemo4(Integer integer, Function<Integer, String> function) {
System.out.println("functionDemo4 --> " + function.apply(integer));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
functionDemo4(1024, integer -> integer.toString() + "程序员节");
}
|
Predicate<T> 断定型接口
表示接收一个参数,判断该参数是否满足某约束,并返回boolean值。该函数式接口方法为boolean test(T t)。
示例1:new一个Predicate实例
static void predicateDemo1() {
Predicate<Integer> predicate = integer -> integer == 1024;
System.out.println("predicateDemo1 --> " + predicate.test(1024));
}
示例2:Predicate做为方法的入参
static void predicateDemo2(Integer integer, Predicate<Integer> predicate) {
System.out.println("predicateDemo1 --> " + predicate.test(integer));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
predicateDemo2(1024, integer -> integer == 1024);
}
|
Consumer<T> 消费型接口
接收一个参数但不返回结果,表示为消费者。该函数式接口方法为void accept(T t)
示例1:new一个Consumer实例
static void consumerDemo1() {
Consumer<Integer> consumer = integer -> System.out.println("consumerDemo1 --> " + integer);
consumer.accept(1024);
}
示例2:Consumer 作为方法的入参
static void consumerDemo2(Integer integer, Consumer<Integer> consumer) {
consumer.accept(integer);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
consumerDemo2(1024, integer -> System.out.println("consumerDemo2 --> " + integer));
}
|
Supplier 供给型接口
与Consumer相反,Supplier只有返回结果,表示为提供者。该函数式接口方法为T get()
示例1:new一个Supplier实例
static void supplierDemo1() {
Supplier<Integer> supplier = () -> 1024;
System.out.println("supplierDemo1 --> " + supplier.get());
}
示例2:Supplier作为方法的入参
static void supplierDemo2(Supplier<Integer> supplier) {
System.out.println("supplierDemo2 --> " + supplier.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
supplierDemo2(() -> 1024);
}
|
函数式接口汇总
| 函数式接口 |
接口类型 |
参数类型 |
返回类型 |
方法 |
Function<T, R> |
函数型接口 |
T |
R |
R apply(T t) |
Predicate<T> |
断定型接口 |
T |
boolean |
boolean test(T t) |
Consumer<T> |
消费型接口 |
T |
void |
void accept(T t) |
Supplier<T> |
供给型接口 |
无 |
T |
T get() |
常见扩展函数式接口
函数型接口
| 函数式接口 |
参数类型 |
返回类型 |
方法 |
用途 |
BiFunction<T,U,R> |
T,U |
R |
R apply(T t, U u) |
接收两个输入参数并产生结果 |
ToIntBiFunction<T,U> |
T,U |
int |
int applyAsInt(T t,U u) |
接收两个输入参数并返回int类型结果 |
ToLongBiFunction<T,U> |
T,U |
long |
long applyAsLong(T t, U u) |
接收两个输入参数并返回long类型结果 |
ToIntFunction<T> |
T |
int |
int applyAsInt(T value) |
接收一个参数并返回int类型结果 |
IntFunction<R> |
int |
R |
R apply(int value) |
接收一个int类型参数,并返回结果 |
IntToDoubleFunction |
int |
double |
double applyAsDouble(int value) |
接收一个int类型参数,返回double类型结果 |
BinaryOperator<T> |
T,T |
T |
T apply(T t1, T t2) |
是BiFunction<T,T,T>的一个子接口,表示对同一类型的两个参数进行操作,产生同一类型的结果 |
UnaryOperator<T> |
T |
T |
T apply(T t) |
是Function<T,T>的一个子接口,表示对单个参数操作,产生同一类型的结果 |
IntUnaryOperator |
int |
int |
int applyAsInt(int operand) |
对单个int值操作,产生一个int结果 |
LongBinaryOperator |
long,long |
long |
long applyAsLong(long left, long right) |
对两个long值计算并产生long结果 |
断定型接口
| 函数式接口 |
参数类型 |
返回类型 |
方法 |
用途 |
BiPredicate<T,U> |
T,U |
boolean |
boolean test(T t, U u) |
接收两个输入参数,断定并返回boolean类型结果 |
IntPredicate |
int |
boolean |
boolean test(int value) |
接收一个int参数值,断定并返回boolean类型结果 |
消费型接口
| 函数式接口 |
参数类型 |
返回类型 |
方法 |
用途 |
BiConsumer<T,U> |
T,U |
void |
void accept(T t, U u) |
接收两个输入参数,不返回结果 |
ObjIntConsumer<T> |
T,int |
void |
void accept(T t, int value) |
接收对象值和int类型参数,不返回结果 |
LongConsumer |
long |
void |
void accept(long value) |
消费long类型值,不返回结果 |
供给型接口
| 函数式接口 |
参数类型 |
返回类型 |
方法 |
用途 |
BooleanSupplier |
无 |
boolean |
boolean getAsBoolean() |
表示供给boolean类型的结果 |
IntSupplier |
无 |
int |
int getAsInt() |
表示供给int类型的结果 |